Sexual Problems
Which Type Diabetes is Worse: Understanding Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. While both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can have severe consequences if not managed properly, it is essential to understand their differences and challenges. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, shedding light on their respective characteristics, management strategies, and potential complications.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Type 1 diabetes usually develops early in life, often during childhood or adolescence.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes remains unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing the condition. Certain viruses and autoimmune disorders can also trigger the onset of type 1 diabetes in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. If these symptoms persist, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. A diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is typically confirmed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels and assess the presence of specific antibodies.
Management and Treatment
Managing type 1 diabetes requires daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump to regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, individuals with type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, maintain a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, and take precautions to prevent complications such as hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes requires constant attention to blood sugar levels, insulin administration, and lifestyle choices. Although managing this condition can be challenging, with the right approach and support, individuals with type 1 diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some essential tips for successfully navigating life with type 1 diabetes:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
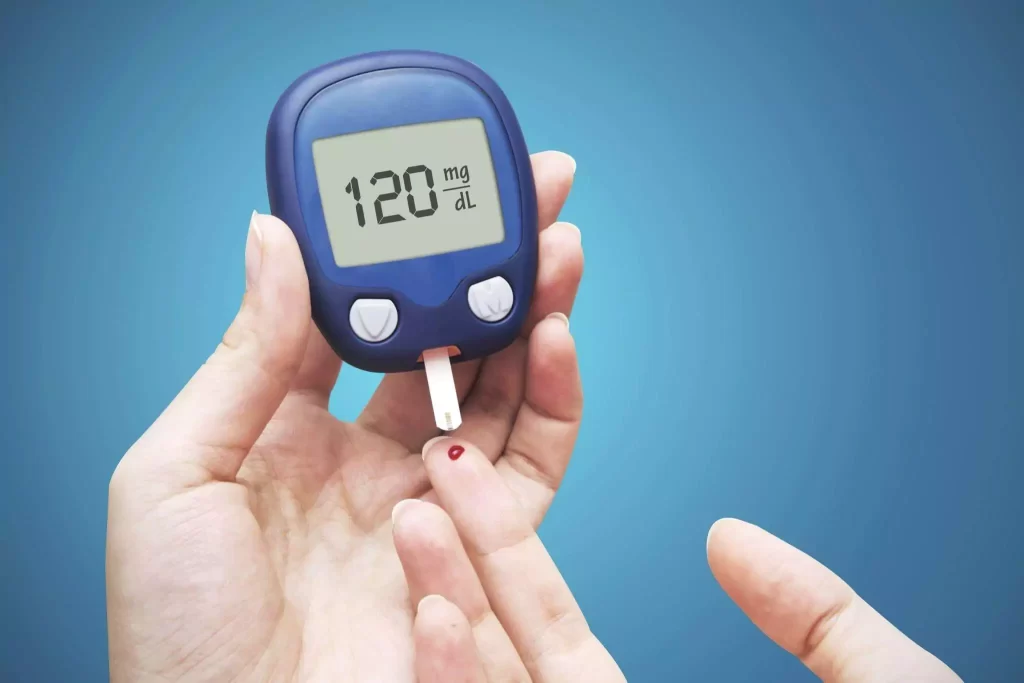

Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is vital for individuals with type 1 diabetes. This allows for a better understanding of how various factors, such as food, physical activity, stress, and medication, affect blood sugar levels. Use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar regularly and keep a record of the results. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine your target range and adjust your management plan accordingly.
2. Administer Insulin Properly
As someone with type 1 diabetes, you will need to administer insulin regularly to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Depending on your treatment plan, this can be done through multiple daily injections or an insulin pump. It is crucial to understand the proper administration technique, including correct dosage calculations and injection sites. Work closely with your healthcare provider or diabetes educator to ensure you are using the right insulin regimen and delivery method for your needs.
3. Plan and Follow a Healthy Diet

Eating a balanced diet is key to managing type 1 diabetes effectively. Consider the following dietary guidelines:
- Carbohydrate Counting: Learn to count carbohydrates as they have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. This can help you adjust your insulin dosage accordingly.
- Balanced Meals: Aim for a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Meal Timing: Establish a regular meal schedule to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid excessive carbohydrate intake.
Consult with a registered dietitian experienced in diabetes management to create a personalized meal plan that suits your needs and preferences.
4. Engage in Regular Physical Activity

Physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Regular exercise can:
- Improve Insulin Sensitivity: Physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently, resulting in better blood sugar control.
- Strengthen Overall Health: Exercise promotes cardiovascular health, weight management, and overall well-being.
- Stabilize Blood Sugar: Engaging in physical activity can help prevent blood sugar fluctuations and reduce the risk of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Before starting an exercise program, consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable activities and any precautions you should take.
5. Seek Support and Education

Living with type 1 diabetes can be challenging both physically and emotionally. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential. Consider the following resources:
- Diabetes Education Programs: Attend diabetes education sessions or workshops to learn more about managing your condition effectively.
- Support Groups: Join local or online support groups to connect with others who have similar experiences. Sharing challenges and successes can provide valuable insights and emotional support.
- Mental Health Support: Pay attention to your emotional well-being and seek professional help if needed. Managing diabetes can be stressful, and addressing mental health is crucial.
Conclusion
Living with type 1 diabetes requires a proactive approach to self-care and regular communication with your healthcare team. By effectively monitoring blood sugar levels, administering insulin properly, following a healthy diet, engaging in physical activity, and seeking support, individuals with type 1 diabetes can lead fulfilling lives. Remember that each person’s experience with diabetes is unique, so it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes

Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent form of diabetes that affects a large number of individuals worldwide. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease, type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. It is essential to understand the characteristics, risk factors, symptoms, management, and potential complications associated with type 2 diabetes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels adequately. Several risk factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, including:
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat can impair insulin function and lead to insulin resistance.
- Lifestyle: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and lack of physical activity, increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and saturated fats can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Family History: Having a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, with type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after the age of 45. This is partly due to the natural decline in physical activity and muscle mass that occurs with ageing.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African-Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, have a higher predisposition to type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be mild or go unnoticed in the early stages. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Increased thirst: Excessive thirst and frequent urination may be early indicators of elevated blood sugar levels.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or lacking energy is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes.
- Frequent infections: Individuals with type 2 diabetes may experience more frequent infections, such as urinary tract infections, yeast infections, or slow-healing wounds.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the lens in the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes typically involves blood tests to measure fasting blood sugar levels, oral glucose tolerance tests, or glycated haemoglobin (A1C) tests.
Management and Treatment
Managing type 2 diabetes focuses on maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and preventing complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is key to managing type 2 diabetes. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, weight management, and stress reduction techniques.
- Oral medications: In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels. These medications work by increasing insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or improving insulin secretion.
- Insulin therapy: As type 2 diabetes progresses, some individuals may require insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
- Regular monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing type 2 diabetes. This helps individuals understand how certain foods, physical activity, medications, and stress levels affect their blood sugar levels.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes
Living with type 2 diabetes requires a proactive approach to managing the condition and making positive lifestyle choices. By incorporating healthy habits into daily life, individuals with type 2 diabetes can effectively control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some practical tips for living well with type 2 diabetes:
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet

A nutritious diet is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Focus on:
- Balanced Meals: Include a variety of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables in your meals.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
- Carbohydrate Awareness: Monitor your carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index.
- Limit Sugary Foods: Minimize the consumption of sugary beverages, desserts, and processed snacks that can cause blood sugar spikes.
Consult a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that suits your dietary needs and diabetes management goals.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity

Exercise offers numerous benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It helps:
- Manage Weight: Regular physical activity aids in weight management and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Control Blood Sugar: Exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake by muscles.
- Boost Overall Health: Physical activity reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, improves circulation, and enhances overall well-being.
Strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, along with strength training exercises two to three times a week. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
3. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels

Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. It helps:
- Track Progress: Monitor how your blood sugar levels respond to various foods, physical activity, and medications.
- Identify Patterns: Recognize trends and patterns in your blood sugar levels to make informed adjustments to your management plan.
- Stay in Control: Regular monitoring empowers you to take necessary actions to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Use a glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider. Keep a record of your readings and discuss them during your regular check-ups.
4. Take Medications as Prescribed

If prescribed medications to manage your diabetes, take them as directed by your healthcare provider. Follow the recommended dosage and timing to ensure their effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels. It is crucial not to skip doses or make changes to your medication regimen without consulting your healthcare provider first.
5. Seek Support and Education

Living with type 2 diabetes can sometimes be challenging. Seek support from:
- Healthcare Team: Regularly visit your healthcare provider and diabetes educator for guidance and assistance.
- Diabetes Support Groups: Join local or online support groups to connect with others who understand your experiences.
- Educational Resources: Stay informed about diabetes management through books, reputable websites, and educational materials.
Knowledge and support can empower you to make informed decisions and stay motivated in managing your condition.
Conclusion
Living with type 2 diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses healthy eating, regular physical activity, medication management, and support. By adopting these strategies, individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their blood sugar levels. Remember to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice based on your specific needs and goals.
Comparing Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
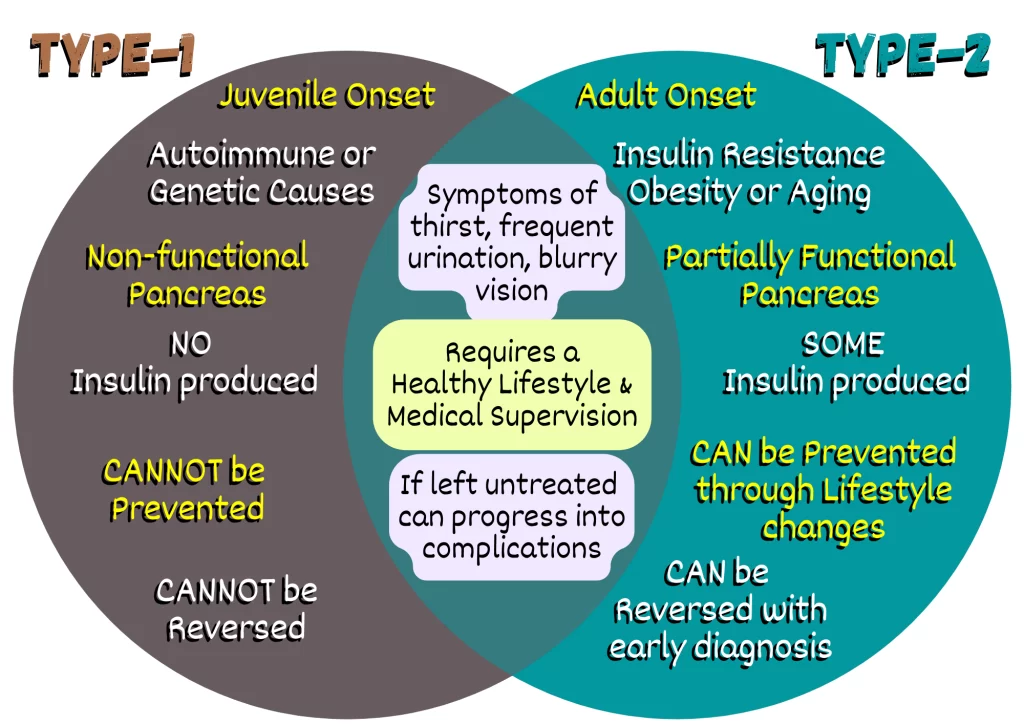
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are two distinct forms of diabetes, each with its own causes, characteristics, and management strategies. Understanding the differences between these two types of diabetes is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and self-care. Here is a comparison of type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
1. Causes and Onset
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood. It often develops in childhood or adolescence, but it can occur at any age.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle choices. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Risk factors include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, family history, and advancing age. Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood, although it is increasingly diagnosed in younger individuals due to the rise in obesity rates.
2. Insulin Dependence
- Type 1 Diabetes: People with type 1 diabetes are entirely dependent on insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump. Since the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas are destroyed, external insulin administration is necessary to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: While some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy, many can manage their condition through lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or non-insulin injectable medications. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas still produces insulin, but the body’s cells become resistant to its effects.
3. Progression and Control
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. It does not have a cure, and insulin therapy is essential for survival. Blood sugar control is crucial to prevent complications. Continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels and insulin adjustments are necessary to maintain stable glucose levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition. It can often be managed initially through lifestyle changes such as weight loss, healthy eating, and regular exercise. In some cases, oral medications or non-insulin injectable medications may be prescribed. However, over time, the disease may progress, and insulin therapy might be required to achieve adequate blood sugar control.
4. Prevalence
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes accounts for approximately 5-10% of all diabetes cases. It is less common compared to type 2 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent form of diabetes, accounting for the majority of cases globally. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing due to rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles.
5. Lifestyle Factors
- Type 1 Diabetes: Although lifestyle choices do not cause type 1 diabetes, individuals with type 1 diabetes still need to maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adhering to insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development and management of type 2 diabetes. Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, can significantly impact blood sugar control and overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is crucial for individuals living with these conditions and healthcare professionals involved in their care. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs primarily in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin dependence. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors, such as obesity and sedentary behaviour, and can be managed through lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or non-insulin injectable medications.
While type 1 diabetes is less prevalent and typically diagnosed at a younger age, type 2 diabetes is more common and can develop in adulthood, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals. Both types of diabetes require proactive management and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels to achieve optimal control and prevent complications.
It is essential for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan that includes proper medication management, adherence to a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and lifestyle modifications as needed. By actively managing their condition and making informed choices, individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Remember, this information serves as a general comparison, and individual experiences may vary. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Complications and Long-Term Effects of Diabetes
Diabetes, whether it is type 1 or type 2, can lead to various complications and long-term effects if not properly managed. Consistently high blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and organs throughout the body. Here are some common complications and long-term effects associated with diabetes:
1. Cardiovascular Disease

Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. The elevated blood sugar levels and associated metabolic changes contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and increase the likelihood of blood clot formation.
2. Kidney Disease

Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is a common complication of diabetes. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to reduced kidney function and potentially end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Regular monitoring of kidney function, blood pressure control, and optimal diabetes management are crucial to minimizing the risk of kidney complications.
3. Eye Complications

Diabetes can cause damage to the small blood vessels in the eyes, leading to various eye problems. These include diabetic retinopathy, which is the leading cause of blindness in adults, as well as cataracts and glaucoma. Regular eye examinations and timely treatment can help prevent or manage these complications.
4. Nerve Damage

Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that commonly affects the feet and legs. It can cause symptoms such as numbness, tingling, pain, and loss of sensation. In severe cases, diabetic neuropathy can lead to foot ulcers and infections, potentially requiring amputation. Good foot care, including regular inspection, proper footwear, and diabetes management, is crucial to prevent or minimize nerve damage.
5. Skin Complications
Individuals with diabetes are more prone to various skin complications, including bacterial and fungal infections. High blood sugar levels provide a favourable environment for the growth of microorganisms. Additionally, diabetes can cause poor circulation, leading to delayed wound healing and an increased risk of skin ulcers.
6. Peripheral Artery Disease
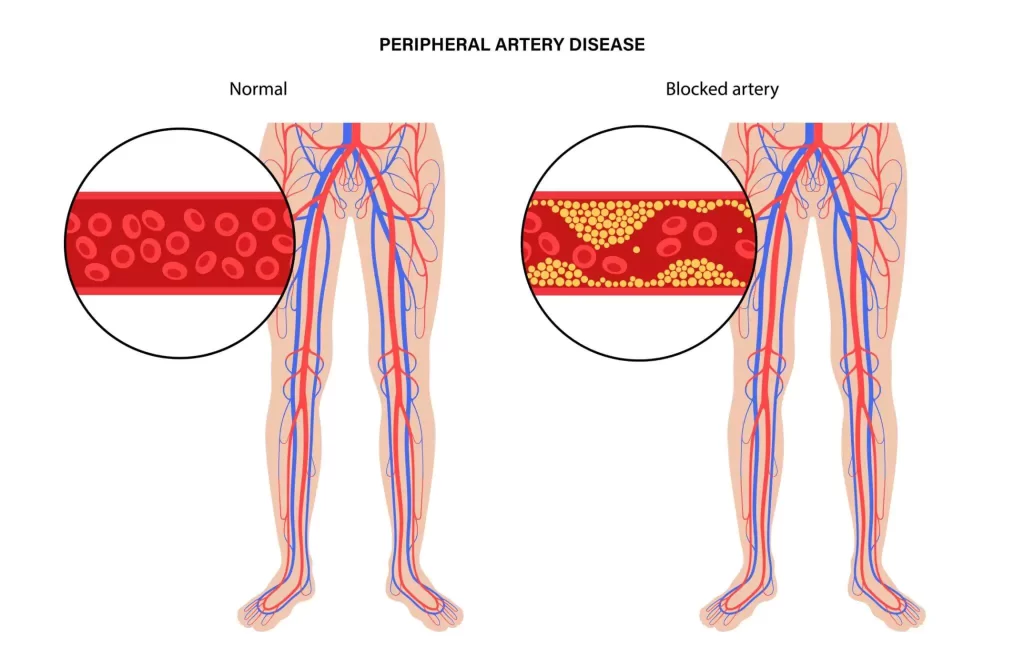
Diabetes increases the risk of peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the limbs, especially the legs. PAD can cause leg pain, cramping, and slow-healing wounds. Lifestyle modifications, medication, and, in some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to manage PAD.
7. Mental Health Issues

Living with diabetes can impact mental health and well-being. The constant management demands, potential complications, and lifestyle changes associated with diabetes can contribute to stress, anxiety, and depression. It is important for individuals with diabetes to seek support from healthcare professionals and engage in self-care practices to maintain good mental health.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires ongoing management and care. Failure to control blood sugar levels can lead to a range of complications and long-term effects. By actively managing diabetes through medication, healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and regular check-ups with healthcare providers, individuals can minimize the risk of developing these complications. It is crucial to maintain a proactive approach to self-care and work closely with healthcare professionals to address any emerging issues promptly.
Remember, each individual’s experience with diabetes is unique, and the risk and severity of complications may vary. Regular communication with your healthcare team and adherence to your prescribed management plan is vital to prevent or managing complications effectively.
Prevention and Lifestyle Recommendations for Diabetes
Preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is possible through adopting healthy lifestyle choices. By making positive changes to your daily habits, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetes and improve your overall well-being. Here are some prevention and lifestyle recommendations:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to prevent type 2 diabetes. Excess body weight, especially around the waistline, increases insulin resistance and the risk of developing diabetes. Focus on a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity to help manage your weight.
2. Follow a Balanced Diet
Adopting a balanced diet is crucial for diabetes prevention. Incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. Be mindful of portion sizes and practice moderation.
3. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in diabetes prevention. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Additionally, incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week. Find activities you enjoy and make them a part of your routine.
4. Avoid Sedentary Behavior
Reduce sedentary behaviour by incorporating more movement throughout the day. Take regular breaks from sitting, whether at work or home and engage in light physical activity. Consider standing at desks, taking the stairs instead of the elevator, or going for short walks during breaks.
5. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can contribute to the development of diabetes. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practising relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation, yoga), engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or seeking professional support if needed.
6. Get Quality Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and diabetes prevention. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your sleep environment is comfortable and conducive to restful sleep.
7. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing diabetes. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit intake to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. Be aware of the calorie content and potential impact on blood sugar levels.
8. Quit Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of developing various health conditions, including diabetes. Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health and can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes and its complications. Seek support from healthcare professionals or support groups to help you quit smoking.
9. Regular Health Check-ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and assess your risk of developing diabetes. They can perform tests such as fasting blood sugar or HbA1c levels to evaluate your glucose metabolism and provide guidance on preventive measures.
10. Know Your Risk Factors
Be aware of your risk factors for diabetes, such as a family history of diabetes, a history of gestational diabetes, or certain medical conditions (e.g., polycystic ovary syndrome). Understanding your risk can help you make informed decisions about lifestyle changes and seek appropriate medical advice.
Conclusion
Preventing diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is possible through adopting a healthy lifestyle. By maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, getting quality sleep, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding smoking, you can significantly reduce your risk.
Advances in Diabetes Research
Over the years, significant progress has been made in diabetes research, leading to a deeper understanding of the disease and advancements in its management and treatment. Researchers and healthcare professionals are constantly striving to improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes. Here are some notable advances in diabetes research:
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Continuous glucose monitoring has revolutionized diabetes management. CGM devices provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day, allowing individuals to track their blood sugar levels more accurately and make timely adjustments to their treatment plans. This technology has improved glycemic control, reduced hypoglycemia, and enhanced quality of life for many people with diabetes.
2. Artificial Pancreas
The development of artificial pancreas systems, also known as closed-loop systems, is a significant breakthrough in diabetes research. These systems combine insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring to automatically regulate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose levels. Artificial pancreas systems mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, providing more precise insulin dosing and reducing the burden of diabetes management.
3. Insulin Delivery Systems
Advancements in insulin delivery systems have improved the convenience and effectiveness of insulin therapy. Innovations include the development of smaller and more discreet insulin pumps, patch pumps, and insulin pens with advanced features for precise dosing and ease of use. These advancements have enhanced insulin delivery options, making it more convenient and flexible for individuals with diabetes.
4. Targeted Therapies
Research has identified specific molecular targets and pathways involved in diabetes, leading to the development of targeted therapies. These therapies aim to address the underlying mechanisms of diabetes and provide more personalized treatment approaches. Examples include medications that target specific receptors or enzymes involved in glucose metabolism and newer classes of antidiabetic drugs with unique mechanisms of action.
5. Islet Cell Transplantation
Islet cell transplantation is an emerging treatment option for individuals with type 1 diabetes. This procedure involves transplanting insulin-producing cells (islets) from a donor pancreas into the recipient’s liver. Islet cell transplantation can restore natural insulin production and improve blood sugar control, reducing or eliminating the need for exogenous insulin injections.
6. Genetic Studies and Precision Medicine
Advances in genetic studies have contributed to a better understanding of the genetic factors influencing diabetes risk and progression. Genome-wide association studies have identified numerous genetic variants associated with diabetes, providing insights into the disease’s genetic basis. This knowledge has paved the way for personalized approaches to diabetes management through precision medicine, tailoring treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic profile.
7. Lifestyle Interventions
Research continues to emphasize the importance of lifestyle interventions in preventing and managing diabetes. Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of structured exercise programs, dietary modifications (such as low-carbohydrate or Mediterranean diets), and behaviour change strategies in achieving glycemic control, weight management, and overall diabetes management.
8. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, particularly in the context of type 1 diabetes, aims to modulate the immune system to prevent or halt the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells. Various approaches, including immune-modulating drugs and vaccines, are being explored to preserve beta cell function and delay the progression of type 1 diabetes.
In conclusion, diabetes is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of people worldwide. However, with advancements in diabetes research, there is a growing understanding of the disease and significant progress in its management and treatment. Continuous glucose monitoring, artificial pancreas systems, targeted therapies, insulin delivery systems, islet cell transplantation, genetic studies, precision medicine, lifestyle interventions, and immunotherapy are among the notable advancements that have improved the lives of individuals with diabetes.
These advancements have brought about more accurate monitoring of blood sugar levels, improved insulin delivery options, personalized treatment approaches based on genetic profiles, and promising developments in preventing or halting the progression of the disease. With continuous research and collaboration, there is hope for even further breakthroughs, including potential cures for diabetes.
It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to stay informed about these advances and work closely with their healthcare providers to incorporate the latest research findings into their management plans. By adopting a proactive approach to diabetes management and taking advantage of these advancements, individuals can strive for better glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
While there is still much to learn and discover, the advancements in diabetes research bring optimism and the promise of a brighter future for those living with the disease. By supporting ongoing research efforts, raising awareness, and advocating for improved diabetes care, we can contribute to the continued progress in understanding, managing, and ultimately finding a cure for diabetes.
Remember, each individual’s journey with diabetes is unique, and it is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to specific needs and circumstances. With a comprehensive approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing support, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage the condition and thrive.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Can diabetes be prevented?
A: While some risk factors for diabetes cannot be changed, such as family history or certain medical conditions, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are key preventive measures.
Q: What are the common symptoms of diabetes?
A: Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections. It’s important to note that symptoms can vary, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all.
Q: Can diabetes be cured?
A: Currently, there is no known cure for diabetes. However, with proper management and lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives. Research efforts are ongoing to find potential cures and more advanced treatment options.
Q: How is diabetes diagnosed?
A: Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure fasting blood sugar levels, oral glucose tolerance tests, or glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) levels. These tests help healthcare professionals assess blood sugar control and determine if an individual has diabetes or prediabetes.
Q: Can diabetes be controlled without medication?
A: In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help control diabetes. However, many individuals with diabetes require medication or insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Q: Are there specific dietary recommendations for diabetes?
A: Yes, dietary recommendations for diabetes include consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is also important to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats. Working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized dietary guidance.
Q: Is it safe for women with diabetes to become pregnant?
A: With proper planning and medical care, women with diabetes can have safe pregnancies and healthy babies. It is essential for women with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to manage their blood sugar levels before and during pregnancy.
Q: Can children develop diabetes?
A: Yes, children can develop diabetes. While type 1 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in children and adolescents, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in youth is also increasing. Early detection, proper management, and support are crucial for children with diabetes.
Q: What are the potential complications of diabetes?
A: Diabetes can lead to various complications over time, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, foot problems, and increased risk of infections. Proper management and regular healthcare follow-ups can help prevent or delay the onset of these complications.
Q: Can exercise help with diabetes management?
A: Yes, regular physical activity is beneficial for diabetes management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, aids in weight management, reduces cardiovascular risk, and improves overall well-being. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise program.
Q: Is diabetes contagious?
A: No, diabetes is not contagious. It is a chronic condition that results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Q: Can stress affect blood sugar levels?
A: Yes, stress can affect blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. Stress hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise, so it’s important to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and support systems.
Q: Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes?
A: Moderate alcohol consumption may be acceptable for some individuals with diabetes, but it’s important to check with a healthcare professional. Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels and interact with diabetes medications, so it’s crucial to drink in moderation and monitor blood sugar levels closely.
Q: Are there alternative treatments for diabetes?
A: While there are no alternative treatments that can replace the medical management of diabetes, some complementary therapies like acupuncture, yoga, and herbal supplements may be used as adjunctive approaches. However, it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into a diabetes management plan.
Q: Can smoking increase the risk of diabetes?
A: Yes, smoking is associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications in individuals with diabetes.
Q: Can diabetes affect mental health?
A: Yes, living with diabetes can impact mental health. The stress of managing the condition, concerns about complications, and the need for lifestyle adjustments can contribute to anxiety and depression. Seeking support from healthcare professionals and joining support groups can help address these challenges.
Q: Can diabetes affect my sex life?
A: Diabetes can affect sexual health, particularly if blood sugar levels are poorly controlled. It may lead to issues like erectile dysfunction in men or decreased libido and vaginal dryness in women. Open communication with healthcare providers can help address these concerns.
Q: Can I travel with diabetes?
A: Yes, individuals with diabetes can travel, but it requires some planning. It’s important to pack adequate supplies, carry necessary medications and prescriptions, have a medical identification card or bracelet, and be aware of time zone changes and the impact on insulin schedules. Consulting with a healthcare professional before travelling is recommended.
Q: Can weight loss help improve diabetes control?
A: Yes, weight loss can significantly improve diabetes control, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Losing excess weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity and improve blood sugar management.
Q: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
A: The frequency of blood sugar monitoring varies depending on the individual’s diabetes management plan. It is typically recommended to check blood sugar levels regularly, including fasting levels, pre-meal levels, and post-meal levels. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized recommendations.
Q: What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
A: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is characterized by insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, while type 2 diabetes is more common in adults.
Q: What is gestational diabetes?
A: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes can lead to insulin resistance. It usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life. Proper management is crucial to ensure a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for diabetes?
A: While lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise, are important for diabetes management, there are no proven natural remedies that can cure or replace medical treatment for diabetes. It’s important to rely on evidence-based medical approaches and consult with healthcare professionals.
Q: What is prediabetes?
A: Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. It serves as a warning sign and an opportunity to make lifestyle changes to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. Regular monitoring and healthy habits are crucial for individuals with prediabetes.
Q: Can diabetes be reversed?
A: While diabetes cannot be completely reversed, lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss, healthy eating, and regular exercise, can help improve blood sugar control and reduce the need for medication in some cases. Early intervention and proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Q: What is insulin resistance?
A: Insulin resistance refers to a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. It is a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes, including weight loss and physical activity, can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage insulin resistance.
Q: Can diabetes lead to other health complications?
A: Yes, diabetes can lead to various health complications if not properly managed. These complications may include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, foot complications, and an increased risk of infections. Consistent monitoring, regular medical check-ups, and adherence to treatment plans are essential for preventing or minimizing complications.
Q: Are there any new medications for diabetes treatment?
A: Yes, there have been several new medications developed for the treatment of diabetes in recent years. These include GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and other novel drug classes that aim to improve blood sugar control, reduce cardiovascular risk, and provide additional benefits beyond glucose management. Healthcare professionals can provide information on these advancements.
Q: Can diabetes affect children and adolescents?
A: Yes, diabetes can affect children and adolescents. Type 1 diabetes is more commonly diagnosed in younger individuals, while type 2 diabetes is becoming increasingly prevalent in this age group, primarily due to rising obesity rates. Early detection, proper management, and support are crucial for young individuals with diabetes.

